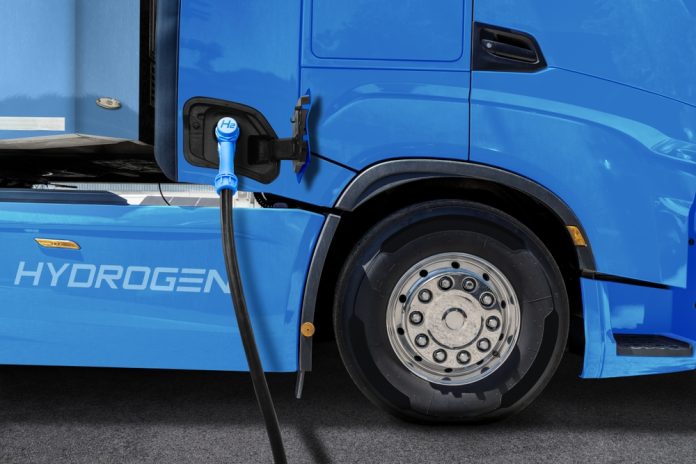
Hydrogen is emerging as a pivotal player in the evolution of heavy and long-haul transport. Its potential lies in offering a cleaner alternative to conventional fossil fuels.
As hydrogen fuel cells gain traction in various vehicles, the logistics landscape is poised for significant transformation.
However, challenges remain in infrastructure development and vehicle efficiency.
The journey towards a hydrogen-powered future is unfolding, raising critical questions about its feasibility and impact on the transport sector.
Why hydrogen? Understanding the case for low-carbon fuel cells
What makes hydrogen a compelling option for low-carbon fuel cells? Hydrogen offers a clean alternative to fossil fuels, producing only water vapour as a byproduct during combustion.
Its abundance in nature, primarily found in water and organic compounds, makes it a sustainable energy source. The high energy density of hydrogen allows for efficient storage and transportation, which is critical for various applications.
Additionally, hydrogen can be generated from renewable resources, such as wind and solar power, further enhancing its low-carbon credentials.
The versatility of hydrogen extends beyond just fuel cells; it can also be integrated into existing energy systems, promoting a gradual transition away from carbon-intensive fuels.
Moreover, advancements in hydrogen production technologies, such as electrolysis and steam methane reforming, are making it increasingly cost-effective.
As global efforts intensify to combat climate change, hydrogen stands out as a pivotal player in achieving a sustainable energy future.
From trucks to trains: Current applications in heavy-duty transport
Hydrogen is increasingly being recognised for its potential in heavy-duty transport applications, including trucks and trains.
Several manufacturers have begun developing hydrogen fuel-cell-powered trucks, offering a clean alternative to traditional diesel vehicles. Companies like Nikola and Hyundai are leading the charge, producing models that can carry significant loads over long distances while emitting only water vapour.
In the rail sector, hydrogen fuel cells are being integrated into locomotives, providing a sustainable solution for freight transport. For instance, Alstom has successfully tested hydrogen-powered trains in Europe, demonstrating their efficiency and reliability in reducing carbon emissions.
These advancements indicate a shift toward adopting hydrogen as a viable energy source in heavy-duty logistics. As technology matures, the role of hydrogen in this sector is expected to expand, contributing to global efforts to decarbonise transport and meet climate targets.
Hydrogen infrastructure: Filling stations, supply chains, and storage challenges
As the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology in transport accelerates, the development of a robust infrastructure becomes essential to support its widespread use. This infrastructure encompasses hydrogen filling stations, supply chains, and effective storage solutions.
Currently, the number of hydrogen refuelling stations remains limited, particularly in rural areas, complicating the logistics for heavy-duty vehicles. Expanding the network of filling stations is crucial to alleviating range anxiety among operators.
Moreover, establishing a reliable supply chain for hydrogen production and distribution poses additional challenges. The integration of renewable energy sources for hydrogen generation, such as electrolysis, must be prioritised to ensure sustainability.
Storage solutions also require innovation, as hydrogen’s low density necessitates advanced methods for safe and efficient containment. Addressing these infrastructure challenges will be vital for the hydrogen economy to thrive, ultimately facilitating the transition to cleaner, more efficient transport options.
Overcoming technical hurdles: Efficiency, safety, and vehicle design
While the potential of hydrogen fuel cells in transportation is immense, several technical hurdles must be addressed to ensure their successful implementation.
Efficiency remains a primary concern; achieving optimal energy conversion from hydrogen to power requires advancements in fuel cell technology. Researchers are focused on enhancing the performance and lifespan of fuel cells to make them more competitive with traditional diesel engines.
Safety is another critical issue, as hydrogen’s flammability poses challenges in vehicle design and storage. Developing robust containment systems and ensuring thorough safety protocols are essential to mitigate risks associated with hydrogen use.
Additionally, vehicle design must adapt to accommodate hydrogen fuel systems while maintaining performance and weight efficiency. Innovations in lightweight materials and compact fuel cell configurations are necessary to create viable heavy-duty vehicles.
Global initiatives: Policies and partnerships driving hydrogen adoption
Recognising the urgent need for sustainable transportation solutions, governments and organisations worldwide are increasingly forming partnerships and implementing policies to facilitate the adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy source.
Numerous countries have set ambitious targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, with hydrogen seen as a pivotal element in achieving these goals. Collaborative efforts, such as the Hydrogen Council and various regional hydrogen initiatives, aim to accelerate research and development while promoting infrastructure investment.
Policies are being established to incentivise the production and utilisation of hydrogen, including subsidies, tax breaks, and grants for research projects.
Additionally, public-private partnerships are fostering innovation by leveraging resources and expertise from multiple sectors. These initiatives not only enhance hydrogen technology but also encourage the integration of hydrogen into existing transport systems, promoting cleaner, more efficient heavy and long-haul transport solutions on a global scale.
Prospects, innovations, and the future of long-haul mobility
The future of long-haul mobility is poised for transformation as innovations in hydrogen technology emerge, promising to redefine transportation efficiency and sustainability. As companies invest in fuel cell technology, the prospect of hydrogen-powered trucks becomes increasingly viable. These vehicles offer extended ranges and rapid refuelling compared to traditional battery-electric options, making them particularly well-suited for long-distance travel.
Research and development efforts focus on improving hydrogen production methods, such as green hydrogen generation from renewable sources, thereby enhancing overall environmental benefits.
Furthermore, advancements in infrastructure, including hydrogen refuelling stations along major transport routes, are critical for widespread adoption.
Collaboration among governments, industry stakeholders, and research institutions is essential to accelerate this transition. By fostering policies that support hydrogen initiatives, the long-haul transport sector stands to achieve significant reductions in carbon emissions and operational costs, heralding a new era of sustainable and efficient mobility.
Paving the way for cleaner logistics
In conclusion, hydrogen is a transformative force in heavy and long-haul transport, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional fuels.
Its integration into various vehicles, backed by global initiatives and infrastructure development, positions hydrogen as a key player in achieving low-carbon mobility.
As challenges related to efficiency, safety, and design are addressed, the future of transport looks promising, with hydrogen paving the way for cleaner logistics and a greener planet.