The NATWORK project is working to build and deploy the first economically realistic, energy-efficient, and viable 6G cybersecurity and resilience framework.
NATWORK aims to set the foundations for and deploy the very first economically realistic, energy-efficient and viable bio-inspired, artificial intelligence (AI) based 6G cybersecurity and resilience framework for intelligent networking and services, taking a holistic approach and considering all elements in a cross-sector business environment to address the diverse requirements and challenges that arise.
The NATWORK vision
The project aims to develop a novel AI-leveraged self-adaptive security mechanism for 6G networks based on resilient biomimicry principles. Our vision spans over six main pillars:
- Definition of a detailed extension to 6G architectures
by providing E2E security. - Fostering secure-by-design composition and migration of novel 6G cloud-native slices and secure distributed computations-network in the edge-to- cloud continuum.
- Provision of net-zero AI-powered trustworthy and explainable management to allow for highly malleable and attack-resilient networks.
- Physical layer security that supports encryption-free, perennial self-resilience of wireless links.
- Deployment and experimental implementation of the security modules in relevant use cases.
- Evaluation, validation, and verification of the security framework performance.
Learning from nature
The NATWORK consortium elaborates on the concept of bio-inspired network key performance indicators (KPIs) management and security. The analogy of a 6G network with a complex biological structure (i.e. the human body) has been employed in NATWORK designs, wherein the immune system is learning from previous security incidents, forecasting potential future threats and adjusting security protocols to accommodate shifting circumstances.
According to this paradigm, 6G network resource management tools optimise service layer agreement (SLA) KPIs and sustainability, as does metabolism with glucose distribution. 6G service security is attained in a sustainable way, like homeostasis, which prevents tissue degradation under threat, selective glucose distribution and iron sequestration to pathogens. In this concept, we embed AI for anomaly detection of unknown new threats, like the self-learning abilities of B- or T-cells.
NATWORK achievements
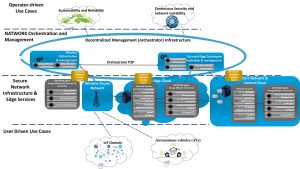
NATWORK’s use cases’ scenarios, requirements, and technical specifications have been formulated along with the first version of the architecture. NATWORK’s architecture imitates the biological immunity’s stepwise operation. Its first defence layer employs AI-based proactive mechanisms that dynamically change the available attack surface to discourage intruders. The second layer uses adaptive AI/ML models to classify detected threats and initiate mitigation actions, while also learning from past security incidents and being trained to forecast and mitigate future threats. This knowledge ensures situational awareness and enhanced adaptability. Thus, NATWORK develops an AI-driven cybersecurity autoimmunity system.
Significant progress has been realised towards the development of the first release of the NATWORK technology. The consortium achieved preliminary results, conducted tests in experimental testbeds and defined the required frameworks for the final integration. These refer to the anticipated outcomes of the technical work, i.e. the components of the envisioned technology, such as: secure-by-design orchestration and management, payload security per runtime, intelligent networking, CTI and explainability, physical layer threat modelling, AI-powered anti-jamming, and RIS defence mechanisms.
Preparatory activities have been conducted towards the initiation of the first round of NATWORK pilots. These include the definition of the evaluation framework and drafting of pilot specifications. The roadmap toward commercial exploitation of the results has been investigated, and partners’ exploitation plans have been elaborated. The results of project activities in the first 18 months have been disseminated through targeted events and 35 scientific publications.
NATWORK also seeks to influence 6G standardisation and policy. The project is aligned with EU regulations like GDPR and the Cybersecurity Act. In addition, the project contributes to the EU’s low-carbon goals by materialising a secure, sustainable, and high-performing 6G ecosystem, hence reinforcing Europe’s global 6G leadership.
Technological developments
NATWORK has developed and continues improving a set of novel technological outcomes. These include:
- Dynamic moving target defence (MTD) framework for end-to-end security.
- AI-native 6G architecture that utilises a cross-layer decentralised approach based on secure federated learning.
- Composer of secure-by-design 6G cloud-native slices.
- Platform-agnostic, always sustainable, all threat coverage, all payload format support, intent-based adjustable security as a service (SECaaS).
- Advanced AI-empowered decentralised orchestration and management services.
- Deep software runtime monitoring for DoS attack detection.
- AI-powered anti-jamming and RIS defence module.
- Decentralised node (self) attestation and trust regulation.
- In-network security and data plane security framework.
Use cases
The consortium has identified four use cases (UCs), further divided into 16 sub-use cases, that allow demonstrating the security framework and a thorough evaluation, validation, and verification of its performance. The NATWORK use cases are:
UC1: Sustainability and reliability of 6G slices and services
The objective of UC1 is to explore innovative energy solutions that can support reliable connectivity and high-quality services while reducing energy costs and minimising environmental impact.
UC2: Anti-jamming technologies for autonomous vehicles
UC2 refers to detection, classification and mitigation of jamming attacks in real-time, utilising machine learning and AI techniques, by analysing signal patterns.
UC3: IoT security
UC3 focuses on the security and privacy of IoT devices and their data in 6G networks, utilising advanced threat detection and mitigation mechanisms.
UC4: Improving variability of network with continuous security
UC4 aims to ensure robust and continuous security in the highly dynamic and heterogeneous 6G network architecture, employing machine learning and AI for real-time security analysis, adaptation, and proactive defence against emerging threats across diverse devices, services, and mobile users.
About the project

NATWORK is implemented by a consortium of 15 participants from eight EU countries and two associated countries (Switzerland and United Kingdom). The project is co-ordinated by the Centre for Research & Technology Hellas – Information Technologies Institute (CERTH-ITI). Its total budget is over €6.1m.
Disclaimer

The project has received co-funding from the Smart Networks and Services Joint Undertaking (SNS JU), under the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme for European participants, the Swiss State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI) for Swiss participants, and the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) for UK participants, under Grant Agreement No. 101139285.
Please note, this article will also appear in the 24th edition of our quarterly publication.









