Christopher Oligschläger, Market Analyst at the European Association of Remote Sensing Companies, gives an overview of the current European Earth observation market and sets out the projections for future growth.
The European downstream Earth observation (EO) market has grown exponentially over the last two decades, with sales increasing close to 10% per annum for the past five years. The market is on a trajectory to ever-wider market uptake and increased commercialisation, and it has been profiting in recent years from important technological developments, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and cloud computing. Products and services built on satellite-based EO data are contributing to the achievement of various relevant international policy goals, such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the European Green Deal, and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.
The European Association of Remote Sensing Companies (EARSC) is determined to contribute to achieving these goals. It works in close collaboration with its large community network and members comprising of more than 130 companies from the sector, spanning from large data to value-added service providers, as well as big corporates, SMEs, and start-ups. Based in Brussels, EARSC is the voice of this European EO downstream industry and maintains close relationships with leading public and private organisations in the field of EO, such as the European Commission and its various thematic Directorate-Generals, the EU Agency for the Space Programme and the European Space Agency (ESA), to represent its members’ interests. EARSC is in constant exchange with sector-specific organisations in Europe and globally to increase awareness for the benefits of EO, support its market uptake, and support internationalisation activities.
COVID-19’s impact on Earth observation
Over the last two years, the COVID-19 pandemic impacted the EO community in two key ways. With all its economic repercussions, the pandemic naturally raised uncertainty in the sector. Whilst some of the companies in the industry had long-term contracts, others feared that expiring contracts might not be extended, resulting in a loss of business. In contrast, several companies reported that the restrictions brought about by the pandemic, such as extensive working from home and widespread quarantines, led to a faster adoption of EO solutions – for instance, in the insurance industries. In this case, EO solutions enabled companies to monitor and assess risks and to check the qualification of damage events and their consequences remotely (e.g., extreme weather events in agriculture). Another industry example is forest management, where rangers increasingly started to monitor their areas of responsibility remotely from their office desks and assign tasks to people on the ground via an EO service.
Labour shortages
Other societal factors influencing market uptake in recent years are related to labour shortages. For example, in agriculture where labour-intensive field inspections and scouting can be conducted remotely, saving time and labour. In addition, several potential user markets are integrating a new generation of employees into their workforce that are more tech-savvy, open to digital tools and more likely to realise the value and benefit of EO services. Acting as change agents in these sectors, these individuals ultimately integrate EO solutions into their daily workflows. This is especially impactful in traditionally conservative industries, such as mining.
Environmental awareness
On top of these challenges, climate change and its associated consequences, such as the impact on oceans, forest decline or higher average temperatures, can be monitored through EO services to derive more informed decisions and implement more targeted counter, mitigation or adaptation measures. EO services cannot only give insights into where and what policy measures should be taken, but can also track, measure and check compliance with corresponding regulations.
Trends in EO uptake
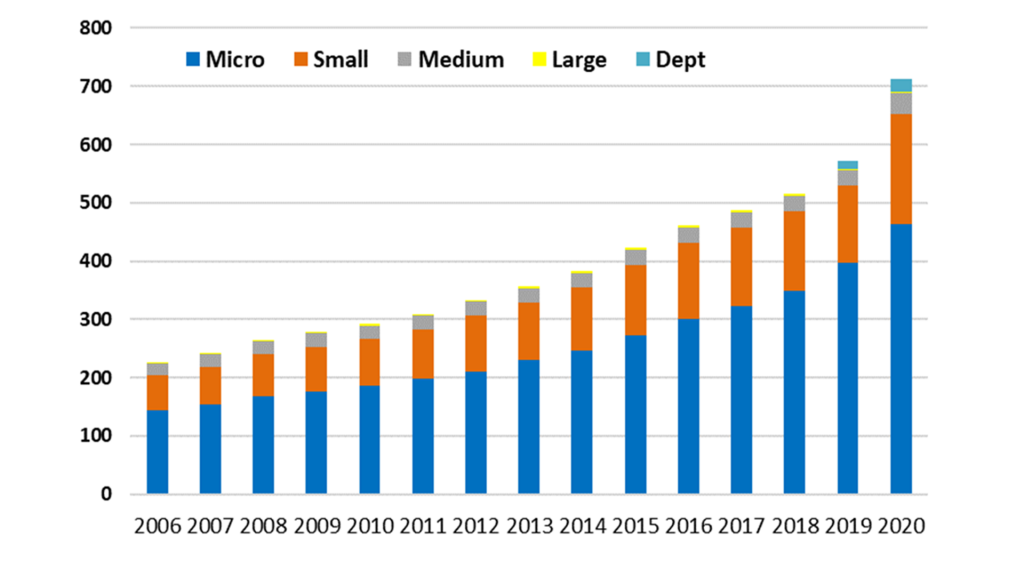
Our 2021 EARSC Industry Survey and Sentinels Benefits Study show that the European EO industry is on track to deliver the insights and solutions needed to meet the various challenges faced by different sectors and policymakers. The EO services industry, that has grown year on year from 572 to 713 companies and 9,800 to 11,600 employees, has increased revenues by an astonishing 24% year on year to €1.71bn. This means a growth of around over 10% has been sustained over the last five years (CAGR). In particular, the last two years before publication of the studies (2019 and 2020) saw a stark acceleration of growth in the number of companies.
Most of the 713 companies (48%) have activities in the area of value-adding services (companies using satellite data to generate products), followed by satellite operators (data sales) with 20%. Interestingly, 26% of the companies mainly trade domestically. Compared to the 2019 survey (37%), this is a significant decrease, suggesting that companies may be focusing more on internationalisation and export activities. Sales to the rest of Europe are at 33% and 11% for both North America and Asia. By far, the most important market sector is defence and security with around 35%, followed by agriculture and environmental ecosystems and pollution with about 12%. Given the strong market share of defence and security, it is no wonder that the public sector (on national and European levels) is the biggest type of customer (46.1%), followed by the private sector (29.2%) and public R&D spending (10.3%). Little change has taken place over the years with regard to revenues split by customer type.
The future of EO uptake
Looking to the future, companies face different barriers to growth, with the most important ones relating to market and user acceptance, acquiring new customers and a lack of development funding. When it comes to customer uptake, the difficulty for customers to be convinced that EO provides them with a business solution is the most important barrier. The lack of awareness of the utility of EO applied to their business processes also represents an important barrier. Looking at various Sentinel Benefits (SeBS) case studies, one can conclude that these doubts or uncertainties on the benefits are often baseless. Various analyses have shown the overarching power of EO services, not only in terms of economic benefits but also with regard to environmental, regulatory, entrepreneurial, scientific and societal benefits. For instance, the switch to an EO solution for winter navigation in the Baltic sea is generating between €24m and €116m per year, in addition to ships saving fuel and time.1 The use of an EO service for precision agriculture in Poland has resulted in economic benefits between €1.1m and €5.3m per year.2 As stated above, often the economic benefits are not the only drivers for integrating EO services into daily workflows. In the Polish case, the use led to dramatic reductions in the use of pesticides and fertilisers benefiting the environment.
Moreover, it is the public agencies or authorities that often have an interest in EO services beyond their financial advantage. In the case of Baden-Württemberg, the State Institute for the Environment is integrating an EO service to monitor the quality of water in lakes throughout their region to an extent that is not possible using traditional sampling and testing, complementing their in situ measurements. This allows the agency to provide a better service for their citizens for a moderate cost, helping to reduce exposure to harmful algal blooms (HABs) whilst improving the environment, reducing pollution and helping nature conservation.3 Besides the Sentinels Benefits Study, there are now numerous other resources and platforms that document and highlight the benefits derived by the use of Copernicus Sentinel data and the European EO services industry (see the EOwiki, NEREUS or EURISY platforms for example).
EO services and products are already playing a crucial role in the transition to a more sustainable and greener planet, and this is expected to increase over the next decade. Looking, for instance, at the European Green Deal, its ambitious goals for the environment and a low-carbon economy call for advanced and innovative services to monitor, analyse, predict, and mitigate the impact of human activity on natural resources (soil, air, water). EO data, combined with in situ and other sets of non-satellite-based data, has become an essential operational instrument to monitor the evolution of the environment and measure progress towards the goals set by the Green Deal and the SDGs. It is imperative to keep raising awareness of the many operational EO services offered by the industry. In that regard, the Green Deal should be an opportunity for the EO sector to play a more significant role and to demonstrate the added value of EO data, especially for policymakers. The main thematics in which EO services are already playing a significant role include climate monitoring; clean, affordable and secure energy; sustainable and smart mobility; farm-to-fork; zero pollution; a toxic-free environment and the overall transition towards a climate-neutral Europe.

Forum for Innovation and Research in European EO
To support these goals and raise awareness for the benefits of EO solutions, EARSC runs several initiatives and activities, one of which is FIRE – the industry-led Forum for Innovation and Research in European EO. Its overall objective is to shape the Research and Innovation Strategy for EO solutions in Europe by fostering exchange between EO and non-EO experts and, in doing so, understanding the various EO information needs and requirements of target markets including agriculture, wind energy, raw materials, infrastructure, marine and urban development. The next FIRE Forum will gather these expert communities on 14 June within EXPANDEO and FIRE Forum, one of the major EO conferences in Europe organised by EARSC. Another major activity EARSC is part of is e-shape, an initiative that develops and promotes European EO capabilities in a user-driven approach, bringing together different communities to increase knowledge and awareness of European EO capabilities. e-shape currently includes 27 cloud-based pilot applications under seven thematic areas to address societal challenges, foster entrepreneurship and support sustainable development, in alignment with the three main priorities of GEO, namely the SDGs, the Paris Agreement and the Sendai Framework. By leveraging Copernicus, e-shape opens new opportunities to develop and expand its use, through existing European capacities, and develop research for business activities.
The Harmonia project
Yet another crucial initiative EARSC is currently involved in, aligned with the SDGs and Green Deal goals, is Harmonia. As the share of the global population living in urban areas is constantly growing, cities need to adapt more effectively to climate change effects, and Harmonia promotes the use of EO in urban environments to tackle these effects. The project is implemented by an international consortium of 22 partners comprising municipalities, research institutes, companies, and academia. It pools together EO services to provide cities and their decision makers with the right insights to make well-informed decisions to foster more resilient cities for a sustainable future.
A positive outlook
To conclude, the EO services industry is on track to help meet major challenges by policymakers, user markets and society at large. Its sustained growth over the last few years, together with increased commercialisation and awareness and adequate support by both the public and private sector, will keep up this momentum. EARSC is determined to support this growth path through its various initiatives and activities and looks forward to connecting and meeting with new potential user markets at EXPANDEO and FIRE Forum 2022.
References
2. earsc.org/sebs/farm-management-support-in-poland/
3. earsc.org/sebs/all-cases/water-quality-management-in-germany/

Christopher Oligschläger
Market Analyst
European Association of Remote Sensing Companies
https://earsc.org
https://www.linkedin.com/company/earsc/
Twitter: @earsc
Please note, this article will also appear in the tenth edition of our quarterly publication.